Time Lost is Brain Lost
Stroke is the second leading cause of death
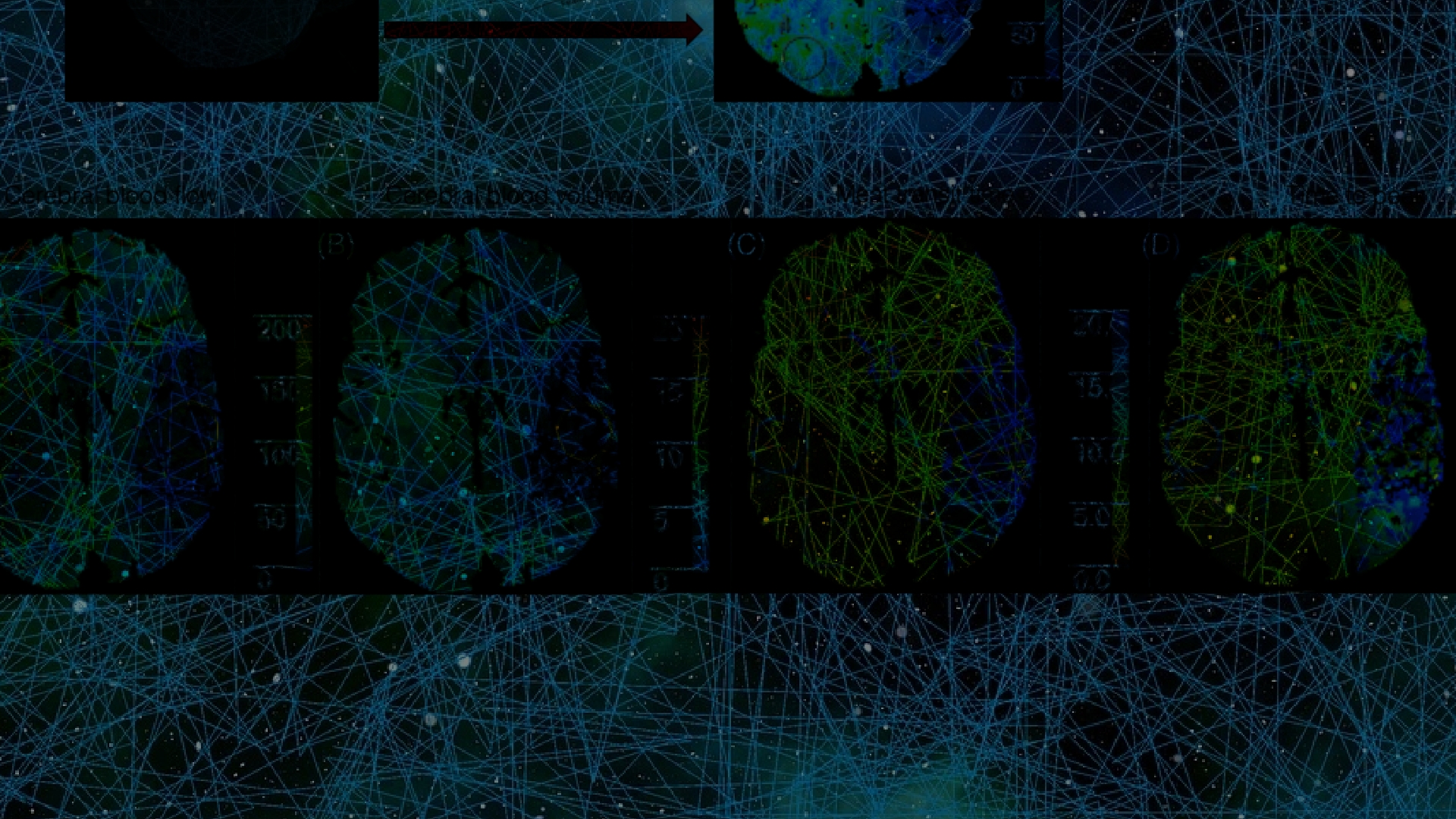
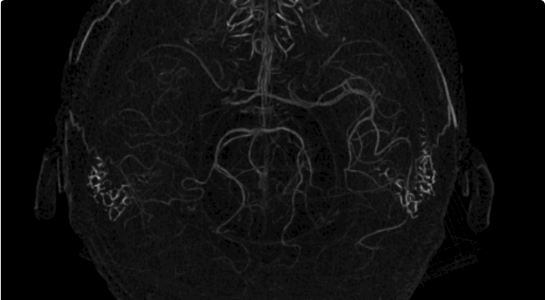
Stroke causes of disability afflicting approximately 800,000 Americans each year. A reduction in the critical brain functin (CBF) below critical thresholds discriminates between salvageable penumbra and irreversible infarct core. The mantra “Time lost is brain lost” emphasizes the rate of nervous tissue loss post-stroke – 1.9 million brain cells lost every minute – and the need for immediate diagnosis and therapeutic interventions. A crucial decision in stroke patient management is the course of treatment to be prescribed: whether a patient should receive a potentially risky and costly thrombolytic intervention, or endovascular procedure and clot retrieval (mechanical thrombectomy).
 Hessam Babaee & Kaveh Laksari
Hessam Babaee & Kaveh Laksari